SC CTSI-Supported Researchers Develop First Fully-Implantable Micropacemaker Designed for Fetal Use
Novel device has received Humanitarian Use Device designation from FDA.
Note: The multidisciplinary research team behind the implantable fetal micropacemaker received support from the SC CTSI Pilot Funding Program, as well as, translational assessment, team building and regulatory support services from SC CTSI’s former Preclinical Translational and Regulatory Support Program.
A team of investigators at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles and the University of Southern California have developed the first fully implantable micropacemaker designed for use in a fetus with complete heart block. The team has done preclinical testing and optimization as reported in a recent issue of the journal Heart Rhythm, and the micropacemaker has been designated a Humanitarian Use Device by the US Food & Drug Administration (FDA). The investigators anticipate the first human use of the device in the near future.
“Up until now, the pacemaker devices that have been used in an attempt to treat this condition in a fetus were designed for adults,” said Yaniv Bar-Cohen, MD, pediatric cardiologist at CHLA and lead author on the paper. “We have lacked an effective treatment option for fetuses.”
With each beat of a healthy heart, an electrical signal moves from the upper to the lower chambers of the heart. As this signal moves, it results in the heart contracting and pumping blood. Congenital heart block is a defect of the heart’s electrical system that originates in the developing fetus, greatly slowing the rate of the heart and impacting its ability to pump blood. Although the condition can be diagnosed in utero, all attempts to treat the condition with a standard pacemaker have failed.
“We now have a pacemaker that can be implanted in utero, potentially without harm to the fetus or the mom,” said Ramen H. Chmait, MD, Director of the CHLA-USC Institute for Maternal-Fetal Health. “This novel device provides a real opportunity to prevent miscarriage and premature birth in babies affected with these abnormalities.”
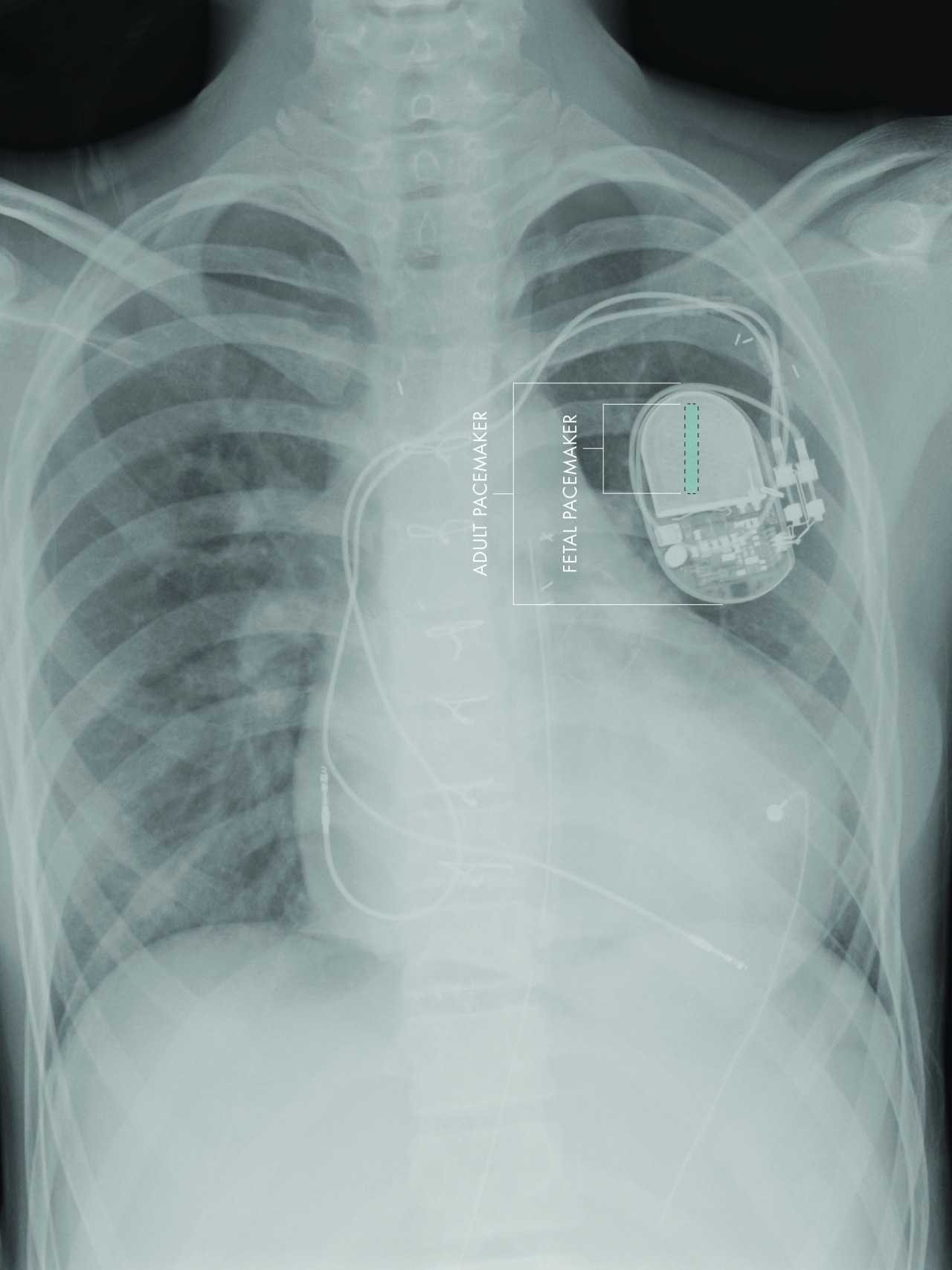
The size of the adult device requires a small part to be implanted in the fetus and the rest to remain externalized. This design has uniformly failed, likely due to fetal movement causing the electrodes to become dislodged from the heart.
“Building on our experience of using microfabrication techniques to create biomedical devices, we have developed a micropacemaker small enough to reside entirely within the fetus,” said Gerald E. Loeb, MD, professor of Biomedical Engineering at the Viterbi School of Engineering at USC. “This will allow the fetus to move freely without risk of dislodging the electrodes.”
Each year, approximately 500 pregnancies in the U. S. are affected by fetal heart block and could be candidates for receiving this device.



